---
sidebar_label: Cursor
slug: /cursor
---
# Integrate OceanBase MCP Server with Cursor
[MCP (Model Context Protocol)](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/introduction) is an open-source protocol introduced by Anthropic in November 2024. It allows large language models to interact with external tools or data sources. With MCP, you do not need to manually copy and execute the output of large language models. Instead, the large language model can directly instruct tools to perform specific actions.
[MCP Server](https://github.com/oceanbase/mcp-oceanbase/tree/main/src/oceanbase_mcp_server) enables large language models to interact with OceanBase Database through the MCP protocol and execute SQL statements. With the right client, you can quickly build project prototypes. The server has been open-sourced on GitHub.
[Cursor](https://cursordocs.com) is an AI-powered code editor that supports multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
This topic demonstrates how to integrate Cursor with OceanBase MCP Server to quickly build a backend application.
## Prerequisites
* You have deployed seekdb.
* You have installed [Python 3.11 or later](https://www.python.org/downloads/) and the corresponding [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/installation/). If your machine has an older version of Python, you can use Miniconda to create a new environment with Python 3.11 or above. For more information, see [Miniconda installation guide](https://docs.anaconda.com/miniconda/install/).
* You have installed [Git](https://git-scm.com//downloads) based on your operating system.
* You have installed the Python package manager uv. After the installation, run the `uv --version` command to verify whether the installation is successful:
```shell
pip install uv
uv --version
```
* You have downloaded [Cursor](https://cursor.com/cn/downloads) and installed the version that matches your operating system. When you use Cursor for the first time, you need to register a new account or log in with an existing one. After logging in, you can create a new project or open an existing project.
## Step 1: Obtain the database connection information
Contact your seekdb deployment engineer or administrator to obtain the database connection string. For example:
```sql
obclient -h$host -P$port -u$user_name -p$password -D$database_name
```
**Parameters:**
* `$host`: The IP address for connecting to seekdb.
* `$port`: The port number for connecting to seekdb. Default is `2881`.
* `$database_name`: The name of the database to access.
:::tip
The connected user must have CREATE, INSERT, DROP, and SELECT privileges on the database.
:::
* `$user_name`: The username for connecting to the database.
* `$password`: The password for the account.
## Step 2: Configure the OceanBase MCP Server
### Clone the OceanBase MCP Server repository
Run the following command to download the source code to your local device:
```shell
git clone https://github.com/oceanbase/mcp-oceanbase.git
```
Go to the source code directory:
```shell
cd mcp-oceanbase
```
### Install dependencies
Run the following command in the `mcp-oceanbase` directory to create a virtual environment and install dependencies:
```shell
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install .
```
### Create a working directory for the Cursor client
Manually create a working directory (such as `cursor`) for the Cursor client and open it with Cursor. The files generated by Cursor will be stored in this directory.
### Add and configure the OceanBase MCP Server
1. Use Cursor V2.0.64 as an example. Click the **Open Settings** icon in the upper-right corner, select **Tools & MCP**, and click **New MCP Server**.

2. Edit the `mcp.json` configuration file.
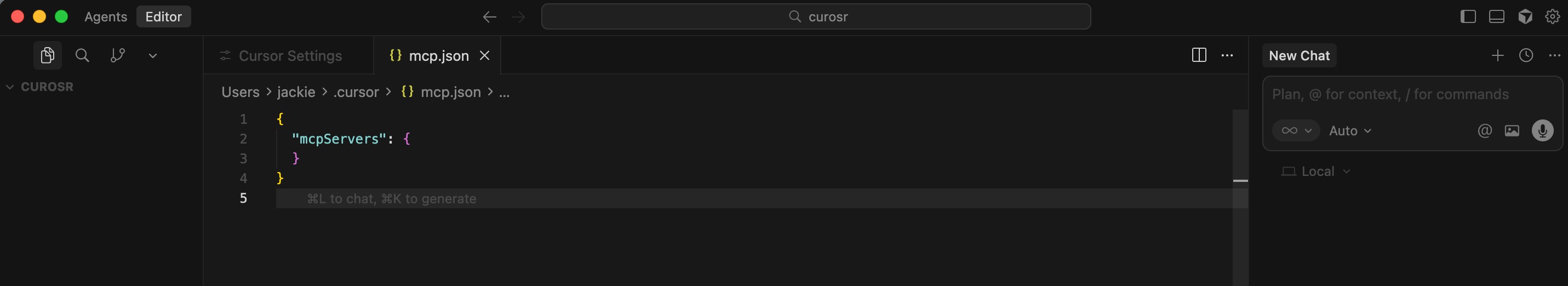
Replace `path/to/your/mcp-oceanbase/src/oceanbase_mcp_server` with the absolute path of the `oceanbase_mcp_server` folder. Replace `OB_HOST`, `OB_PORT`, `OB_USER`, `OB_PASSWORD`, and `OB_DATABASE` with the corresponding information of your database:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"oceanbase": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/path/to/your/mcp-oceanbase/src/oceanbase_mcp_server",
"run",
"oceanbase_mcp_server"
],
"env": {
"OB_HOST": "***",
"OB_PORT": "***",
"OB_USER": "***",
"OB_PASSWORD": "***",
"OB_DATABASE": "***"
}
}
}
}
```
3. If the configuration is successful, the MCP Server is displayed in ready status.
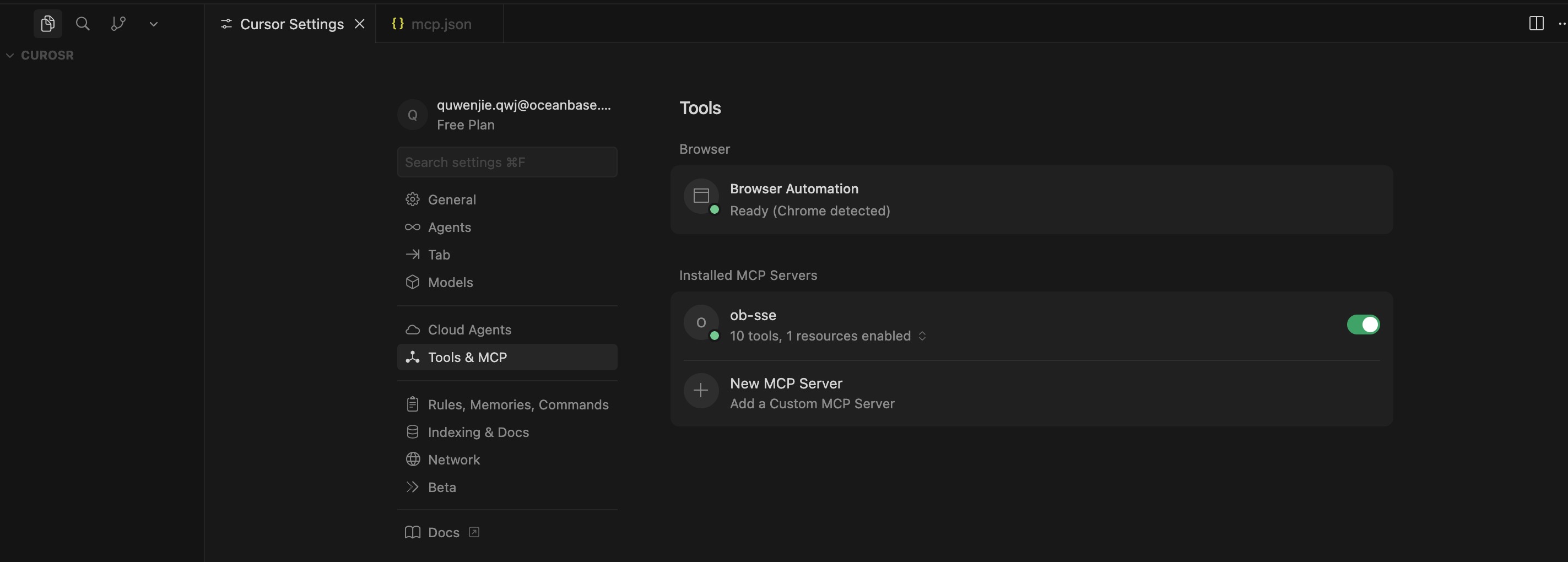
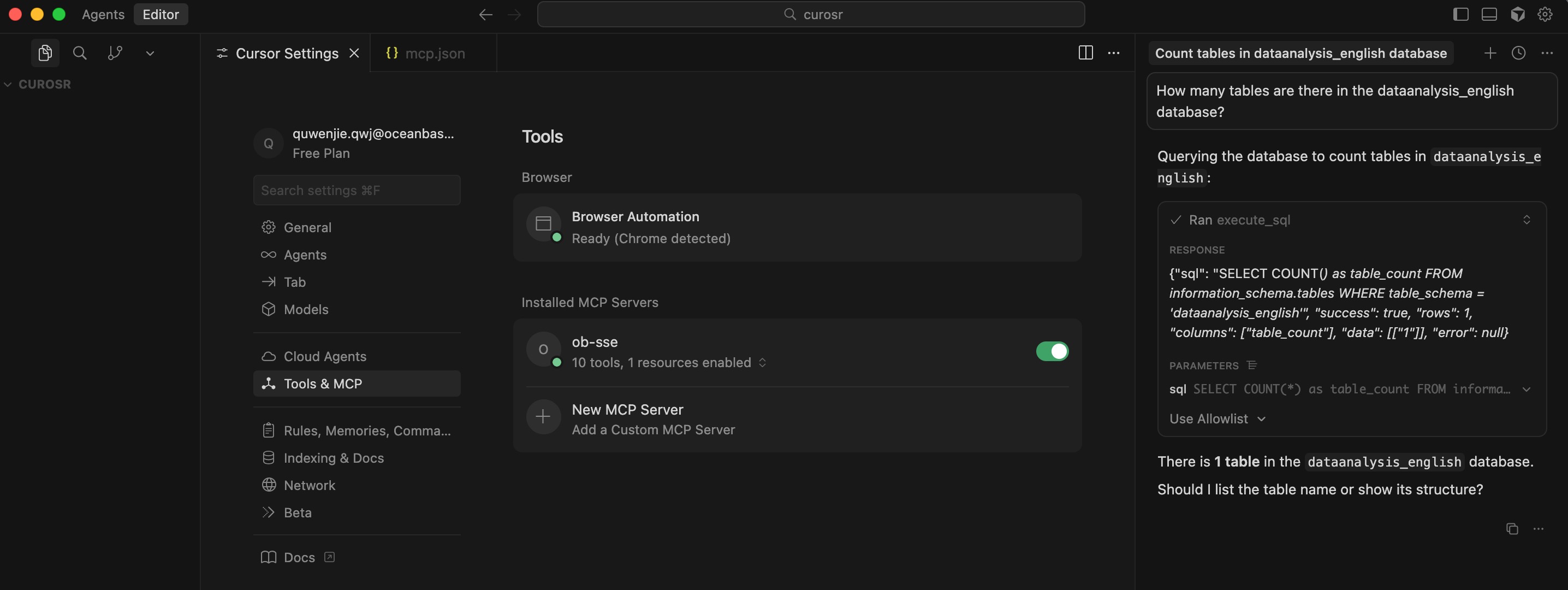
### Test the MCP Server
1. In the chat dialog box, enter the prompt: `How many tables are there in the dataanalysis_english database?`. The Cursor client will display the SQL statement to be executed. Confirm that it is correct and click the `Run` button to execute the query. The Cursor client will display all the table names in the `dataanalysis_english` database, indicating that we have successfully connected to seekdb.
### Use FastAPI to quickly create a RESTful API project
You can use FastAPI to quickly create a RESTful API project. FastAPI is a Python web framework for building RESTful APIs.
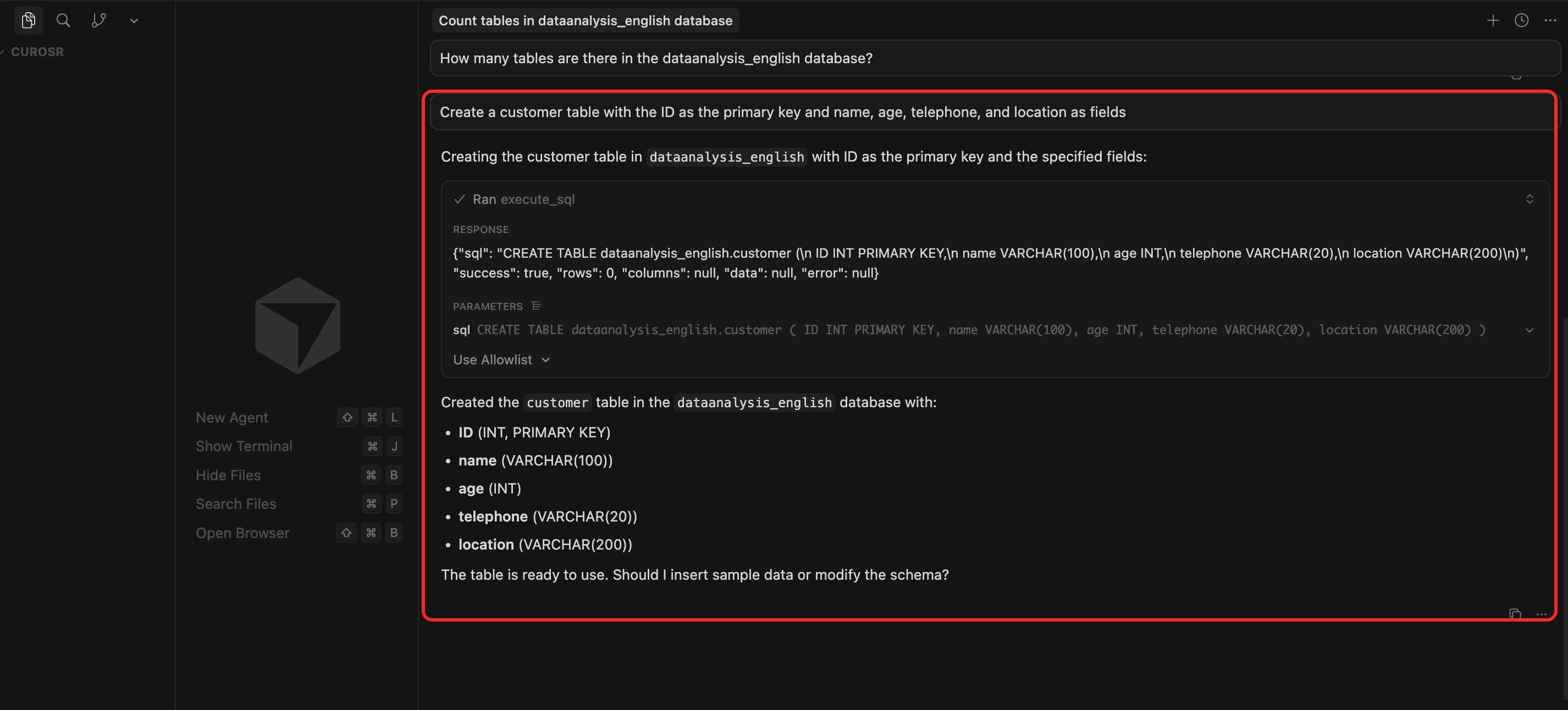
1. Create a customer table
In the dialog box, enter the prompt: `Create a customer table with the ID as the primary key and name, age, telephone, and location as fields`, confirm the SQL statement, and click `Run` to execute the query.
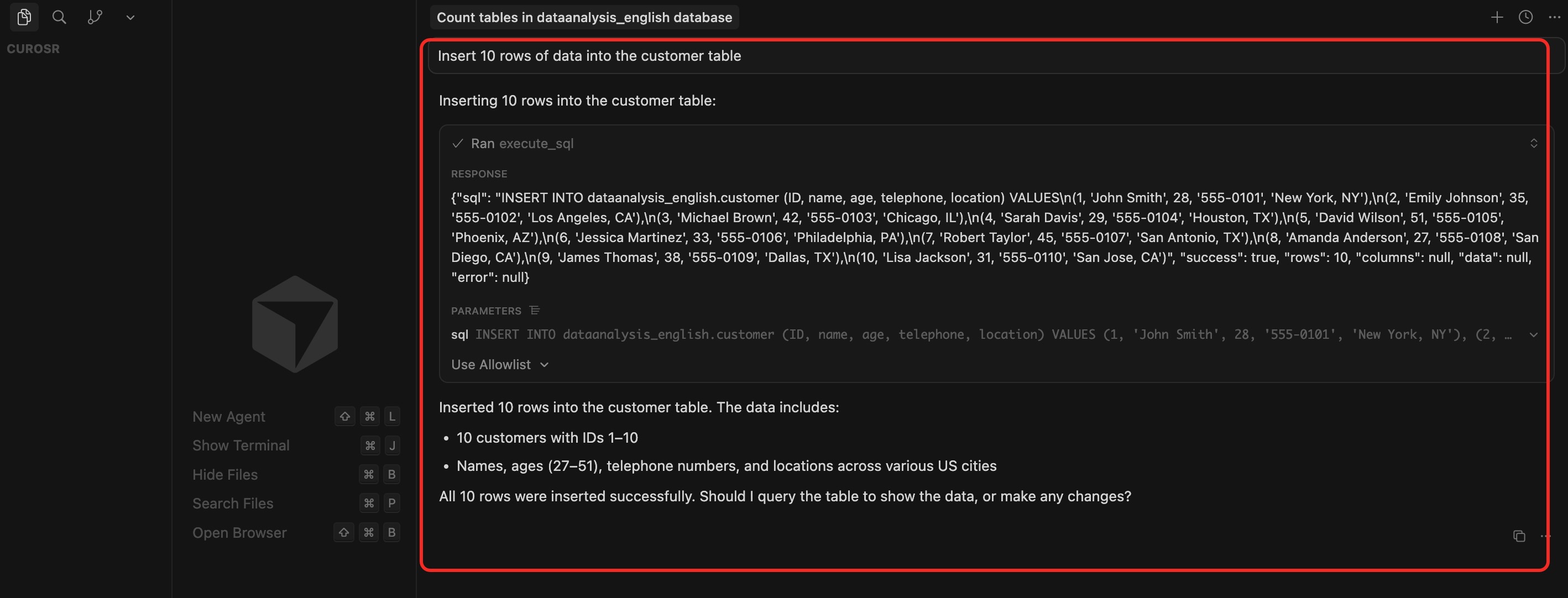
2. Insert test data
In the dialog box, enter the prompt: `Insert 10 rows of data into the customer table`, confirm the SQL statement, and click `Run` to execute the query. After the data is inserted, a message will be displayed: `Inserted 10 rows into the customer table. The data includes...`.
3. Create a FastAPI project
In the dialog box, enter the prompt: `Create a FastAPI project and generate a RESTful API based on the customer table`, confirm the SQL statement, and click `Run` to execute the query.
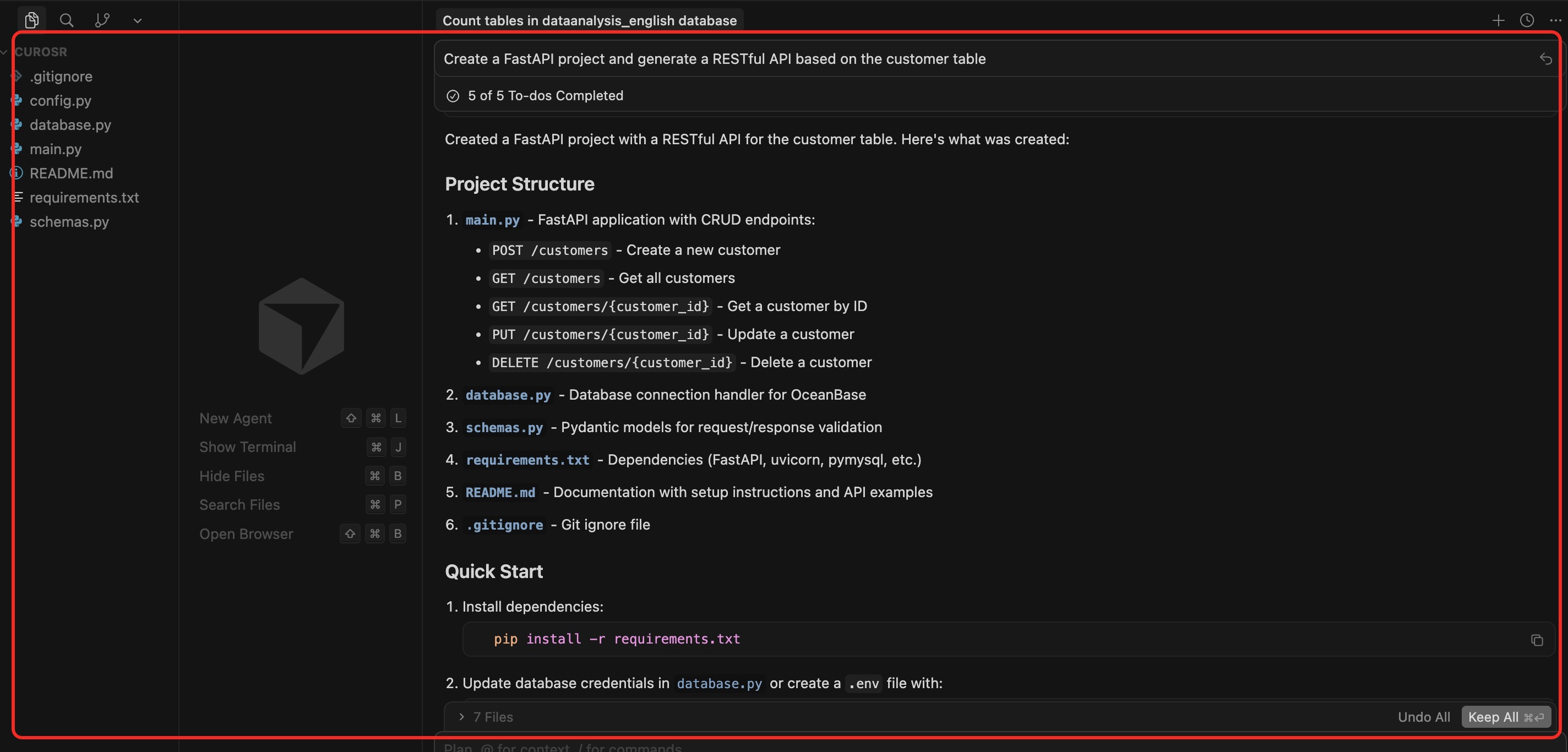
This step will automatically generate necessary files. It is recommended to select `Accept All` for the first use, because the content of the files generated by AI may be uncertain, and you can adjust them as needed later.
4. Create a virtual environment and install dependencies
Execute the following command to use the uv package manager to create a virtual environment and install the dependencies in the current directory:
```shell
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install -r requirements.txt
```
5. Start the FastAPI project
Execute the following command to start the FastAPI project:
```shell
uvicorn main:app --reload
```
6. View the data in the table
Run the following command in the command line or use other request tools to view the data in the table:
```shell
curl http://127.0.0.1:8000/customers
```
The return result is as follows:
```json
[{"ID":1,"name":"John Smith","age":28,"telephone":"555-0101","location":"New York, NY"},{"ID":2,"name":"Emily Johnson","age":35,"telephone":"555-0102","location":"Los Angeles, CA"},{"ID":3,"name":"Michael Brown","age":42,"telephone":"555-0103","location":"Chicago, IL"},{"ID":4,"name":"Sarah Davis","age":29,"telephone":"555-0104","location":"Houston, TX"},{"ID":5,"name":"David Wilson","age":51,"telephone":"555-0105","location":"Phoenix, AZ"},{"ID":6,"name":"Jessica Martinez","age":33,"telephone":"555-0106","location":"Philadelphia, PA"},{"ID":7,"name":"Robert Taylor","age":45,"telephone":"555-0107","location":"San Antonio, TX"},{"ID":8,"name":"Amanda Anderson","age":27,"telephone":"555-0108","location":"San Diego, CA"},{"ID":9,"name":"James Thomas","age":38,"telephone":"555-0109","location":"Dallas, TX"},{"ID":10,"name":"Lisa Jackson","age":31,"telephone":"555-0110","location":"San Jose, CA"}]
```
You can see that the RESTful APIs for creating, deleting, updating, and querying data have been successfully generated:
```shell
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Depends
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import List
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Column, Integer, String
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, Session
# seekdb connection configuration (modify it as needed)
DATABASE_URL = "mysql://***:***@***:***/***"
engine = create_engine(DATABASE_URL, echo=True)
SessionLocal = sessionmaker(autocommit=False, autoflush=False, bind=engine)
Base = declarative_base()
class Customer(Base):
__tablename__ = "customer"
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, index=True)
name = Column(String(100))
age = Column(Integer)
telephone = Column(String(20))
location = Column(String(100))
class CustomerCreate(BaseModel):
id: int
name: str
age: int
telephone: str
location: str
class CustomerUpdate(BaseModel):
name: str = None
age: int = None
telephone: str = None
location: str = None
class CustomerOut(BaseModel):
id: int
name: str
age: int
telephone: str
location: str
class Config:
orm_mode = True
def get_db():
db = SessionLocal()
try:
yield db
finally:
db.close()
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/customers/", response_model=CustomerOut)
def create_customer(customer: CustomerCreate, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
db_customer = Customer(**customer.dict())
db.add(db_customer)
try:
db.commit()
db.refresh(db_customer)
except Exception as e:
db.rollback()
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail=str(e))
return db_customer
@app.get("/customers/", response_model=List[CustomerOut])
def read_customers(skip: int = 0, limit: int = 100, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
return db.query(Customer).offset(skip).limit(limit).all()
@app.get("/customers/{customer_id}", response_model=CustomerOut)
def read_customer(customer_id: int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
customer = db.query(Customer).filter(Customer.id == customer_id).first()
if customer is None:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Customer not found")
return customer
@app.put("/customers/{customer_id}", response_model=CustomerOut)
def update_customer(customer_id: int, customer: CustomerUpdate, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
db_customer = db.query(Customer).filter(Customer.id == customer_id).first()
if db_customer is None:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Customer not found")
for var, value in vars(customer).items():
if value is not None:
setattr(db_customer, var, value)
db.commit()
db.refresh(db_customer)
return db_customer
@app.delete("/customers/{customer_id}")
def delete_customer(customer_id: int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
db_customer = db.query(Customer).filter(Customer.id == customer_id).first()
if db_customer is None:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Customer not found")
db.delete(db_customer)
db.commit()
return {"ok": True}
```