Initial commit
This commit is contained in:
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
slug: /build-kb-in-seekdb
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Build a knowledge base desktop application based on seekdb
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial guides you through building a MineKB (Mine Knowledge Base, personal local knowledge base) desktop application using seekdb, demonstrating how to implement intelligent Q&A through vector search and large language models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Core features of the application:
|
||||
* Multi-project management: Supports creating multiple independent knowledge base projects.
|
||||
* Document processing: Supports multiple formats such as TXT, MD, PDF, DOC, DOCX, and RTF, with automatic text extraction and vectorization.
|
||||
* Intelligent search: Based on seekdb's vector indexes (HNSW), enabling efficient semantic search.
|
||||
* Conversational Q&A: Query the knowledge base through AI conversations to obtain accurate answers based on document content.
|
||||
* Local storage: All data is stored locally to protect privacy and security.
|
||||
|
||||
Reasons for choosing seekdb:
|
||||
* Embedded deployment: Embedded as a library in the application, no independent service required.
|
||||
* Native vector support: Built-in vector type and HNSW indexes, improving vector search performance by 10-100x.
|
||||
* All-in-One: Supports transactions, analytics, and vector search simultaneously, meeting all requirements with one database.
|
||||
* SQL interface: Standard SQL syntax, developer-friendly.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment requirements
|
||||
|
||||
The following environment is required for developing and running the knowledge base desktop application:
|
||||
|
||||
* Operating system: Linux supported, Ubuntu 20.04+ recommended.
|
||||
* Node.js: 16.x+ supported, for frontend development, 18.x LTS recommended.
|
||||
* Rust: 1.70+ supported, required by Tauri, 1.75+ recommended.
|
||||
* Python: 3.x+ supported, 3.9+ recommended.
|
||||
|
||||
### Technology stack and dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
* Frontend technology stack (see `package.json` for details)
|
||||
* `@tauri-apps/api`: Tauri frontend API for calling Rust commands
|
||||
* `@radix-ui/*`: Accessible UI component library
|
||||
* `react-markdown`: Markdown rendering
|
||||
* `react-syntax-highlighter`: Code highlighting
|
||||
* `lucide-react`: Icon library
|
||||
* Backend technology stack (see `Cargo.toml` for details)
|
||||
* `tauri`: Tauri framework core
|
||||
* `tokio`: Async runtime
|
||||
* `reqwest`: HTTP client (for calling AI APIs)
|
||||
* `pdf-extract`, `docx-rs`: Document parsing
|
||||
* `nalgebra`: Vector computation
|
||||
|
||||
### Python dependencies (see `requirements.txt` for details)
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
seekdb==0.0.1.dev4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Install seekdb
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure seekdb is installed and verify the installation:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install seekdb -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
|
||||
# Verify installation:
|
||||
python3 -c "import seekdb; print(seekdb.__version__)"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### API key configuration
|
||||
|
||||
MineKB requires Alibaba Cloud Bailian API to provide embedding and LLM services. Register an [Alibaba Cloud Bailian](https://bailian.console.aliyun.com/) account, enable model services, and obtain an API key.
|
||||
|
||||
After obtaining the API key, fill it in the configuration file: `src-tauri/config.json`
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"api": {
|
||||
"dashscope": {
|
||||
"api_key": "<sk-your-api-key-here>",
|
||||
"base_url": "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/api/v1",
|
||||
"embedding_model": "text-embedding-v1",
|
||||
"chat_model": "qwen-plus"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"database": {
|
||||
"path": "./mine_kb.db",
|
||||
"name": "mine_kb"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
<ul><li>Qwen LLM provides a certain amount of free usage quota. Please monitor your free quota usage during use, as exceeding it will incur charges.</li><li>This tutorial uses Qwen LLM as an example to introduce how to build a Q&A bot. You can also choose to use other LLMs. If you use another LLM, you need to update the <code>apiKey</code>, <code>model</code>, and <code>baseUrl</code> parameters in the <code>src-tauri/config.example.json</code> file.</li></ul>
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Run the application locally
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Build and start
|
||||
|
||||
1. Clone the project and install dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# Clone the project
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ob-labs/mine-kb.git
|
||||
cd mine-kb
|
||||
|
||||
# Install frontend dependencies
|
||||
npm install
|
||||
# Install Python dependencies
|
||||
pip install seekdb==0.0.1.dev4 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Configure the API key.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cp src-tauri/config.example.json src-tauri/config.json
|
||||
# Edit the configuration file and fill in your API key
|
||||
nano src-tauri/config.json
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Start the application.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
npm run tauri:dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
<!---->
|
||||
|
||||
When a user starts the MineKB application, the system executes the following initialization flow in sequence:
|
||||
* Application initialization (see `src-tauri/src/main.rs` for code details)
|
||||
* Initialize the logging system
|
||||
* Determine the application data directory
|
||||
* Load the configuration file
|
||||
* Initialize the Python environment
|
||||
* Initialize the seekdb database
|
||||
* Initialize the database schema
|
||||
* Create application state
|
||||
* Start the Tauri application
|
||||
* Frontend initialization (see `src/main.tsx` for code details)
|
||||
* Mount the React application
|
||||
* Call the list_projects command to get the project list
|
||||
* Render the project panel and conversation panel
|
||||
* Wait for user operations
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Create a knowledge base
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend using seekdb documentation for testing. [Click here](https://github.com/oceanbase/seekdb-doc).
|
||||
|
||||
<!---->
|
||||
|
||||
After the user clicks the `Create Project` button, the system executes the following flow:
|
||||
* Frontend interaction implementation
|
||||
* See `ProjectPanel.tsx` for code details
|
||||
* Backend processing implementation
|
||||
* See `commands/projects.rs` for code details
|
||||
* Database operations
|
||||
* See `services/project_service.rs` for code details
|
||||
* Database layer (`seekdb_adapter.rs` → `Python Bridge` → `seekdb`), code as follows:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# Python bridge receives command
|
||||
{
|
||||
"command": "execute",
|
||||
"params": {
|
||||
"sql": "INSERT INTO projects (...) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
|
||||
"values": ["uuid-here", "My Project", "Description", "active", 0, "2025-11-05T...", "2025-11-05T..."]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert to seekdb SQL
|
||||
cursor.execute("""
|
||||
INSERT INTO projects (id, name, description, status, document_count, created_at, updated_at)
|
||||
VALUES ('uuid-here', 'My Project', 'Description', 'active', 0, '2025-11-05T...', '2025-11-05T...')
|
||||
""")
|
||||
conn.commit()
|
||||
|
||||
# Return success response
|
||||
{
|
||||
"status": "success",
|
||||
"data": null
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In summary, creating a knowledge base performs the following tasks:
|
||||
1. Generate a unique project ID (UUID v4).
|
||||
2. Validate the project name (non-empty, no duplicates).
|
||||
3. Initialize the project status as Active.
|
||||
4. Record creation time and update time.
|
||||
5. Write project information to the `projects` table in seekdb.
|
||||
6. Commit the transaction to ensure data persistence.
|
||||
7. Return project information to the frontend.
|
||||
8. Frontend updates the project list and displays the new project.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Start a conversation
|
||||
|
||||
<!---->
|
||||
|
||||
After the user enters a question in the dialog box, the system executes the following flow:
|
||||
* Frontend sends message
|
||||
* See `ChatPanel.tsx` for code details
|
||||
* Backend processing
|
||||
* See `commands/chat.rs` for code details
|
||||
* Vector search
|
||||
* See `services/vector_db.rs` for code details
|
||||
* LLM streaming call
|
||||
* See `services/llm_client.rs` for code details
|
||||
|
||||
In summary, starting a conversation performs the following tasks:
|
||||
1. User enters a question.
|
||||
2. Save the user message to the database.
|
||||
3. Call Alibaba Cloud Bailian API to generate a query vector (1536-dimensional).
|
||||
4. Execute vector search in seekdb (using HNSW index).
|
||||
5. Get the top 20 most similar document chunks.
|
||||
6. Calculate similarity scores and filter (threshold 0.3).
|
||||
7. Use relevant documents as context.
|
||||
8. Build a prompt (context + user question).
|
||||
9. Streamingly call LLM to generate an answer.
|
||||
10. Send the answer to the frontend in real-time for display.
|
||||
11. Save the AI reply and source information to the database.
|
||||
12. Update the last update time of the conversation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary
|
||||
|
||||
### Advantages of seekdb in desktop application development
|
||||
|
||||
Through the MineKB project practice, seekdb demonstrates the following significant advantages in building desktop applications.
|
||||
|
||||
#### High development efficiency
|
||||
|
||||
| Comparison item | Traditional solution | seekdb solution |
|
||||
| :----------- | :----------------------- | :--------------------------- |
|
||||
| Database deployment | Requires installing and configuring an independent service | Embedded, no installation required |
|
||||
| Vector search implementation | Manually implement vector indexes and search algorithms | Native HNSW indexes, ready to use |
|
||||
| Data management | Manage relational data and vector data separately | Unified management, SQL interface |
|
||||
| Cross-platform support | Need to compile/package database for different platforms | `pip install` automatically adapts to platform |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Excellent performance
|
||||
|
||||
Vector search performance test (10,000 document chunks, 1536-dimensional vectors):
|
||||
|
||||
| Operation | seekdb (HNSW) | SQLite (manual search) | Improvement |
|
||||
| :---------- | :------------ | :---------------- | :------- |
|
||||
| Top-10 search | 15ms | 1200ms | 80x |
|
||||
| Top-20 search | 25ms | 2500ms | 100x |
|
||||
| Top-50 search | 45ms | Cannot complete | ∞ |
|
||||
|
||||
Reason analysis:
|
||||
* HNSW index: O(log N) complexity, efficient search.
|
||||
* Native vector type support: No serialization overhead, improved performance.
|
||||
* Columnar storage optimization: Only read required fields, reducing I/O.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Data privacy and security
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description | Value |
|
||||
| :------- | :----------------------- | :------------- |
|
||||
| Local storage | Database files stored on user devices | Zero privacy leakage |
|
||||
| No network required | All operations offline except AI conversations | Sensitive documents not uploaded |
|
||||
| User control | Users can backup and migrate database files | Data ownership belongs to users |
|
||||
| ACID transactions | Ensures data consistency | No data loss |
|
||||
|
||||
#### All-in-One capabilities
|
||||
|
||||
seekdb's integrated capabilities provide unlimited possibilities for future expansion:
|
||||
* Relational data management: Projects, documents, sessions, etc.
|
||||
* Transaction support: ACID features.
|
||||
* Vector search: Semantic search.
|
||||
* Full-text search: Use seekdb's `FULLTEXT INDEX`.
|
||||
* Hybrid search: Combines semantic search and keyword search.
|
||||
* Analytical queries: Use OLAP capabilities for knowledge statistics.
|
||||
* External table queries: Directly query external files such as CSV.
|
||||
* Smooth upgrade: Data can be migrated to OceanBase distributed edition.
|
||||
|
||||
### MineKB project summary
|
||||
|
||||
Through the MineKB project, we have proven that seekdb + Tauri is an excellent combination for building AI-Native desktop applications.
|
||||
|
||||
Key success factors:
|
||||
1. seekdb: Provides powerful vector search capabilities.
|
||||
2. Tauri: Provides a lightweight cross-platform desktop application framework.
|
||||
3. Python Bridge: Achieves seamless integration between Rust and seekdb.
|
||||
4. RAG architecture: Fully leverages the advantages of vector search.
|
||||
|
||||
Applicable scenarios:
|
||||
* Personal knowledge base management
|
||||
* Enterprise document retrieval systems
|
||||
* AI-assisted programming tools
|
||||
* Study notes and research assistants
|
||||
* Any desktop application that requires semantic search
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,281 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
slug: /build-multi-model-application-based-on-oceanbase
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Build a cultural tourism assistant with seekdb multi-model integration
|
||||
|
||||
This topic demonstrates how to build your cultural tourism assistant using seedb's multi-model integration technology.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, we build an attraction recommendation application through seekdb's multi-model integration of spatial data and vector search. This application can use hybrid search of GIS and vector data to find related attractions, combined with a large language model (LLM) Agent workflow to implement a simple travel planning assistant.
|
||||
|
||||
## How it works
|
||||
|
||||
* **Spatial data processing technology**: GIS systems provide precise geographic positioning and optimal route planning.
|
||||
|
||||
* **Vector data processing technology**: Uses a pre-trained model (BGE-m3) to convert unstructured data of attractions into vector representations, and leverages seedb's vector search capabilities to efficiently process similarity searches.
|
||||
|
||||
* **Large language model Agent technology**: At the intelligent interaction level, uses LLM Agent technology combined with Prompt Engineering to understand user intent and enable multi-turn conversations, achieving task decomposition and planning. This enhances the system's interactive experience, accurately understanding your needs and providing personalized services.
|
||||
|
||||
* **Content-based recommendation algorithm**: Combines collaborative filtering and content-based recommendation algorithms, incorporating contextual information such as season and ratings to achieve personalized recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
## Concepts
|
||||
|
||||
:::collapse
|
||||
|
||||
* **Multi-model integration**: Multi-model integration is an important capability of seekdb. In this topic, multi-model integration mainly refers to multi-model data hybrid search technology. seekdb supports integrated queries across vector data, spatial data, document data, and scalar data. With support for various indexes—including vector indexes, spatial indexes, and full-text indexes—it provides high-performance hybrid search capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
<!--  -->
|
||||
|
||||
* **Large Language Model (LLM)**: A large language model is a deep learning model trained on vast amounts of text data. It can generate natural language text or understand the meaning of language text. Large language models can handle various natural language tasks, such as text classification, question answering, and conversation, making them an important pathway toward artificial intelligence.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
* You have deployed seekdb. For more information about deploying seekdb, see [Deployment overview](../../400.guides/400.deploy/50.deploy-overview.md).
|
||||
|
||||
* You have created a database. For more information about creating a database, see [Create a database](https://en.oceanbase.com/docs/common-oceanbase-database-10000000001971662).
|
||||
|
||||
* Vector search is enabled. For more information about vector search, see [Perform vector search by using SQL statements](https://www.oceanbase.com/docs/common-oceanbase-database-cn-1000000002012934).
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET ob_vector_memory_limit_percentage = 30;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* (Recommended, not required) Install [Python 3.10 and later](https://www.python.org/downloads/) and the corresponding [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/installation/). If your machine has a low Python version, you can use Miniconda to create a new Python 3.10 or later environment. For more information, see [Miniconda installation guide](https://docs.anaconda.com/miniconda/install/).
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
conda create -n obmms python=3.10 && conda activate obmms
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Install [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/). You can refer to the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 -m ensurepip
|
||||
python3 -m pip install poetry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Install the required Python packages. You can refer to the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install python-dotenv tqdm streamlit pyobvector==0.2.16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Obtain the LLM API key
|
||||
|
||||
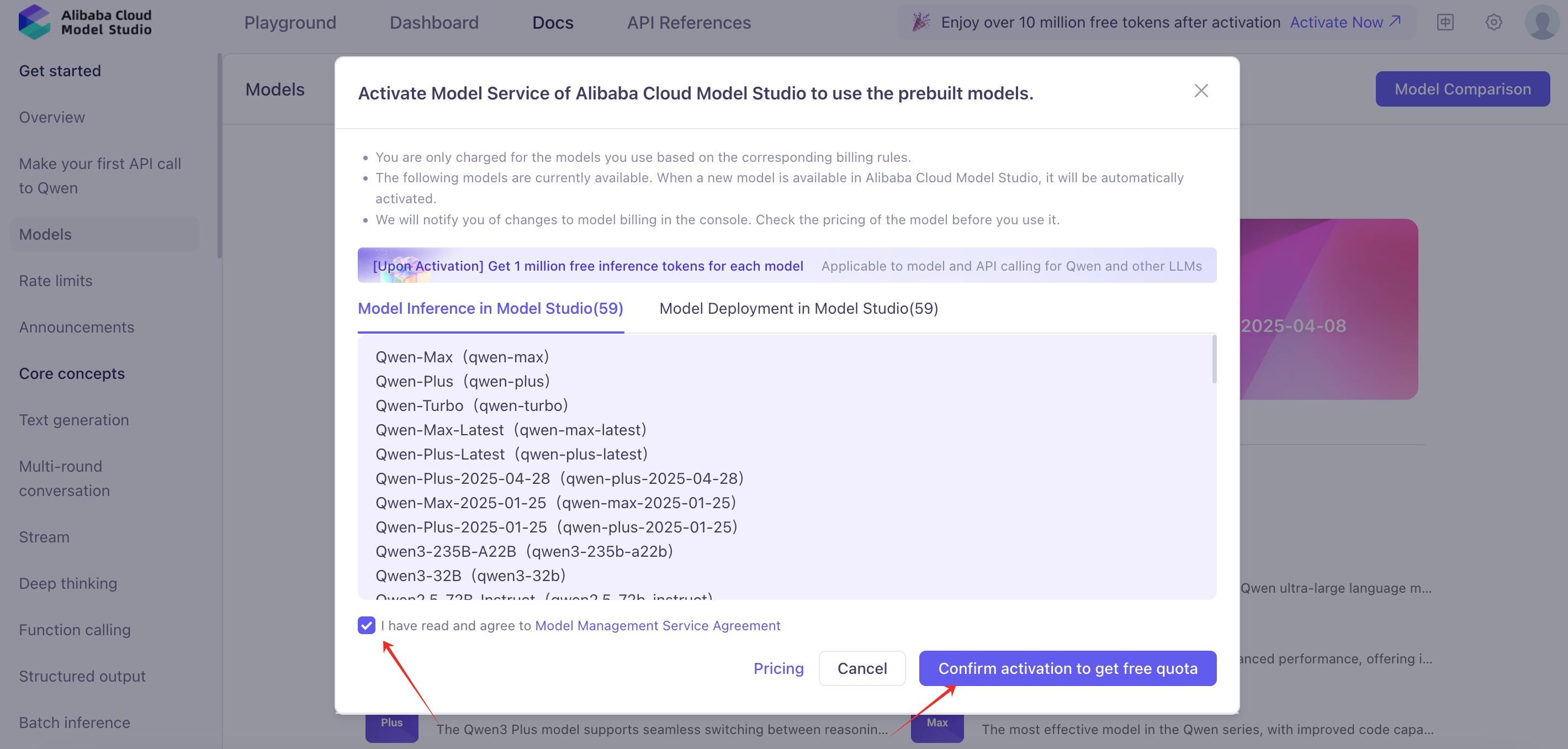
1. Register for an account with [Alibaba Cloud Model Studio](https://bailian.console.alibabacloud.com/), activate the model service, and obtain an API key.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
<!--  -->
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Obtain a geographic service API key
|
||||
|
||||
Register on the Amap (Gaode) Open Platform and obtain an API key for the [Basic LBS service](https://obbusiness-private.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/doc/img/cloud/tutorial/%E9%AB%98%E5%BE%B72.jpg).
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- 
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
 -->
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3: Download the public dataset
|
||||
|
||||
Download the [China City Attraction Details](https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/audreyhengruizhang/china-city-attraction-details) dataset from Kaggle.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 4: Build your cultural tourism assistant
|
||||
|
||||
### Clone the project repository
|
||||
|
||||
1. Clone the latest project repository.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/oceanbase-devhub/ob-multi-model-search-demo.git
|
||||
cd ob-multi-model-search-demo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Move the downloaded `archive` dataset ZIP package to the `ob-multi-model-search-demo` project folder, rename it to `citydata`, and decompress it.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# Please modify the path to the actual location of archive.zip.
|
||||
mv ./archive.zip ./citydata.zip
|
||||
unzip ./citydata.zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Install dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command in the project root directory to install dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
poetry install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Set environment variables
|
||||
|
||||
Set the environment variables in the `.env` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
vim .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You need to update the `OB_`-prefixed variables with your database connection information, and manually add the following variables: update `DASHSCOPE_API_KEY` with the API key obtained from the Alibaba Cloud Tongyi Lab console, and update `AMAP_API_KEY` with the API key obtained from the Alibaba Cloud AMap API service. Then, save the file.
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
# Host address in the database connection string
|
||||
OB_URL="******" ## Format: IP:<port>
|
||||
OB_USER="******" ## Username
|
||||
OB_DB_NAME="******" ## Database name
|
||||
# Password in the database connection string
|
||||
OB_PWD="******"
|
||||
# Optional SSL CA file path in the database connection string. If you do not need SSL encryption, remove this parameter.
|
||||
OB_DB_SSL_CA_PATH="******"
|
||||
|
||||
# Manually add LLM API key
|
||||
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY="******"
|
||||
# Manually add Amap API key
|
||||
AMAP_API_KEY="******"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Import data
|
||||
|
||||
In this step, we will import the data from the downloaded dataset into seekdb.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
For the first build, we recommend that you select only a portion of the data (such as attractions starting with the letter A) for import. Importing all data will take a long time.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python ./obmms/data/attraction_data_preprocessor.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If the following progress is displayed, the data is being successfully imported.
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
...
|
||||
./citydata/Changde.csv:
|
||||
100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 100/100 [00:04<00:00, 20.77it/s]
|
||||
./citydata/Weinan.csv:
|
||||
100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 90/90 [00:13<00:00, 6.54it/s]
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Start the UI chat interface
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command to start the chat interface:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
poetry run streamlit run ./ui.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If no web page is directly displayed, you can visit the URL shown in the terminal to open the tourism assistant application.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
You can now view your Streamlit app in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
Local URL: http://localhost:8501
|
||||
Network URL: http://172.xxx.xxx.xxx:8501
|
||||
External URL: http://172.xxx.xxx.xxx:8501
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- ## Application display
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Dependency installation issues
|
||||
|
||||
#### Poetry installation failure
|
||||
|
||||
If the `poetry install` command fails, try the following steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Update Poetry to the latest version:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install --upgrade poetry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clear the Poetry cache:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
poetry cache clear --all pypi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Reinstall dependencies:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
poetry install --no-cache
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment configuration issues
|
||||
|
||||
#### Python environment not activated
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
Make sure you have activated the correct Python environment (such as the obmms conda environment) before installing dependencies.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you have activated the correct conda environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
conda activate obmms
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Python version incompatibility
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you are using Python 3.10 or later:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python --version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If the version is too low, recreate the environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
conda create -n obmms python=3.10
|
||||
conda activate obmms
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Database connection issues
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter database connection issues, check:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Whether the database connection information in the `.env` file is correct
|
||||
2. Whether seekdb is running normally
|
||||
3. Whether the network connection is normal
|
||||
4. Whether the database user has sufficient privileges
|
||||
|
||||
### Other common issues
|
||||
|
||||
#### Port occupied
|
||||
|
||||
If Streamlit prompts that the port is occupied when starting, you can specify another port:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
poetry run streamlit run ./ui.py --server.port 8502
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Insufficient memory
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter memory issues during data import, you can:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Reduce the batch import data volume
|
||||
2. Increase system memory
|
||||
3. Adjust seekdb memory configuration
|
||||
|
||||
#### API key issues
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you have correctly configured:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Alibaba Cloud Bailian API key (DASHSCOPE_API_KEY)
|
||||
2. Amap API key (AMAP_API_KEY)
|
||||
|
||||
API keys can be configured in the `.env` file.
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
slug: /build-image-search-app-in-seekdb
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Build an image search application based on seekdb
|
||||
|
||||
## Background information
|
||||
|
||||
In the information explosion era, users often need to quickly retrieve necessary information from massive amounts of data. Efficient retrieval systems are required to quickly locate content of interest in online literature databases, e-commerce product catalogs, and rapidly growing multimedia content libraries. As the amount of data continues to increase, traditional keyword-based search methods cannot meet users' needs for both accuracy and speed. This is where vector search technology comes in. It encodes different types of data, such as text, images, and audio, into mathematical vectors and performs search operations in the vector space. This allows the system to capture the deep semantic information of data and provide more accurate and efficient search results.
|
||||
|
||||
This topic shows you how to build your image search application using seekdb's vector search technology.
|
||||
|
||||
## Image search architecture
|
||||
|
||||
The image search application stores a library of images as vectors within a database. Users can upload the image they want to search for through the UI interface. The application then converts the image into a vector, searches for similar vectors in the database, and returns the results. The similar images are displayed on the UI interface.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
* You have deployed seekdb.
|
||||
|
||||
* You have created a database. For more information about how to create a database, see [Create a database](https://en.oceanbase.com/docs/common-oceanbase-database-10000000001971662).
|
||||
|
||||
* The vector search feature is enabled for the database. For more information about the vector search feature, see [Perform fast vector search by using SQL](https://en.oceanbase.com/docs/common-oceanbase-database-10000000001976352).
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET ob_vector_memory_limit_percentage = 30;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Prepare the images you need. If you do not have enough images for testing, you can refer to image datasets from major open-source websites.
|
||||
* You have installed Python 3.9 or later.
|
||||
|
||||
* You have installed Poetry.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 -m ensurepip
|
||||
python3 -m pip install poetry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Procedure
|
||||
|
||||
1. Clone the code repository.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://gitee.com/oceanbase-devhub/image-search.git
|
||||
cd image-search
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
poetry install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Set environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cp .env.example .env
|
||||
# Update the database information in the .env file
|
||||
vi .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Update the contents of the `.env` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com
|
||||
|
||||
DB_HOST="127.0.0.1" ## Set the server IP address
|
||||
DB_PORT="2881" ## Set the port
|
||||
DB_USER="root" ## Set the tenant and username
|
||||
DB_NAME="test" ## Set the database name
|
||||
DB_PASSWORD="" ## Set the tenant user password
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Upload the prepared images to the server.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Start the image search program.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
poetry run streamlit run --server.runOnSave false image_search_ui.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The return result is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
Collecting usage statistics. To deactivate, set browser.gatherUsageStats to false.
|
||||
|
||||
You can now view your Streamlit app in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
Local URL: http://localhost:8501
|
||||
Network URL: http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8501
|
||||
External URL: http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8501
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Open the image search UI interface. Open the corresponding URL from step 5 based on your actual situation.
|
||||
7. Under **Image Loading Settings**, enter the absolute path of the directory where images are stored on the server in **Image Loading Directory**.
|
||||
8. Click **Load Images**.
|
||||
9. After the images are loaded, you can perform image search operations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Application demo
|
||||
|
||||
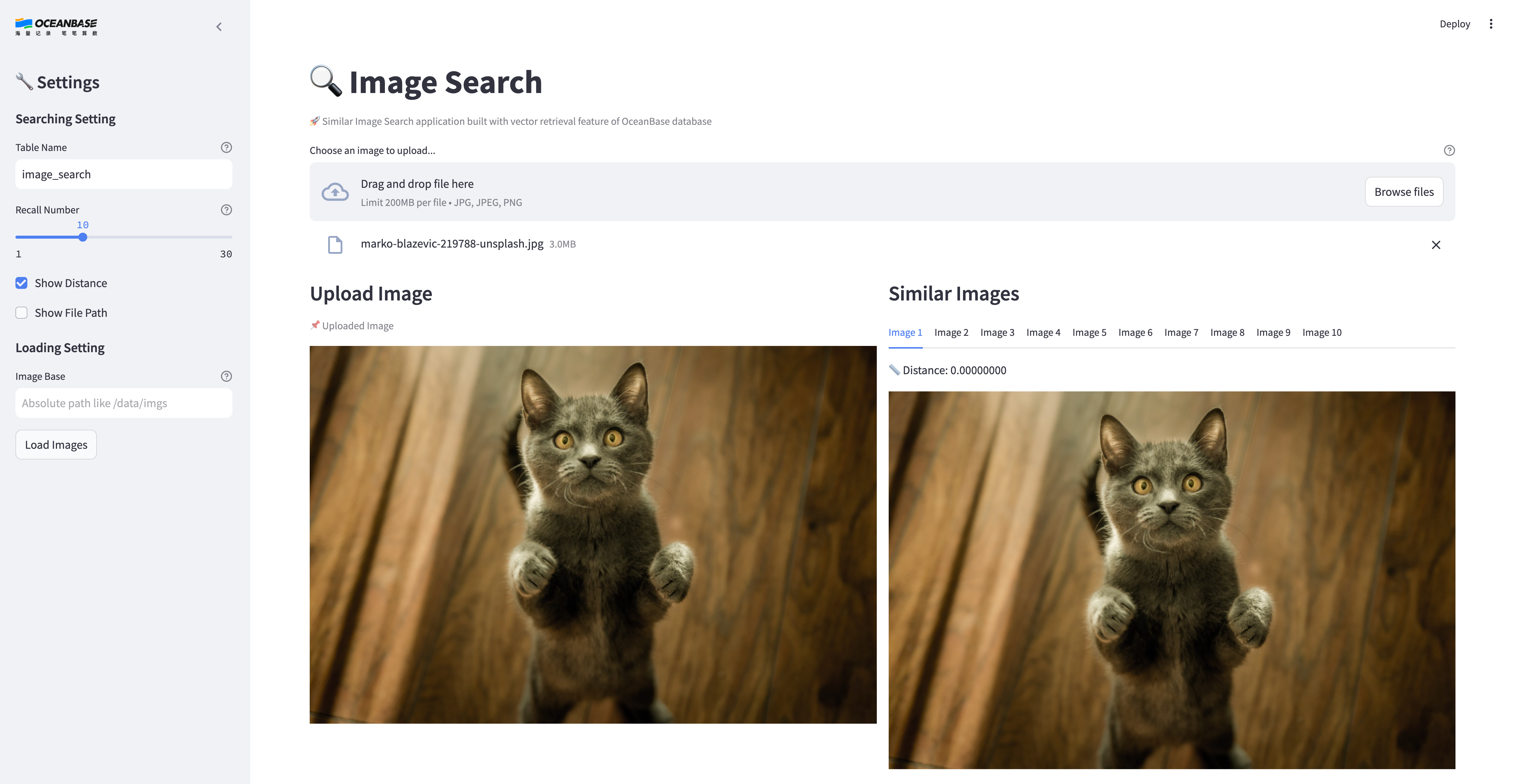
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user